Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy
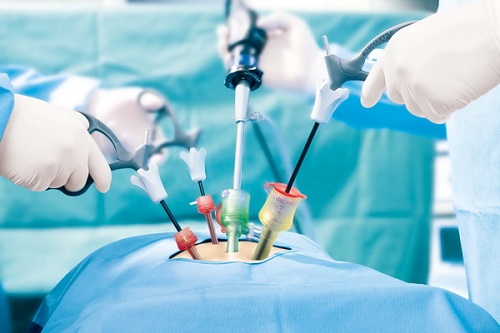
Laparoscopy & Hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a commonly performed gynecologic procedure to evaluate the endometrial cavity. This article focuses on the procedure of diagnostic hysteroscopy.
Broadly, 2 systems of diagnostic hysteroscopy exist: panoramic (also known as direct optical) and contact (also known as contact microhysteroscopy). Modern references to hysteroscopy usually imply a panoramic technique in which the uterine cavity is distended with liquid or gas and evaluated with the hysteroscope
ysteroscopy is also used to examine the uterine cavity before women undergo in vitro fertilization. A slender instrument called a hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina and into the uterine cavity to look inside.
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Exploratory laparoscopy (also referred to as diagnostic laparoscopy) is a minimally invasive method for the diagnosis of intra-abdominal diseases through direct inspection of intra-abdominal organs. Exploratory laparoscopy also allows tissue biopsy, culture acquisition, and a variety of therapeutic interventions. Laparoscopic ultrasonography (LUS) can also be performed during exploratory laparoscopy to evaluate organs that are not amenable to direct visual inspection.
The advent of laparoscopic surgery represents a landmark in surgery that initiated a shift from the era of open abdominal surgery to the minimally invasive surgery revolution. Today, laparoscopy is the most common and preferred method for addressing a number of routine and complex surgical procedures, such as cholecystectomy, appendectomy, splenectomy, adrenalectomy, and others
Laparoscopic Cystectomy
Laparoscopic Cystectomy is the removal of ovarian cysts. An oophorectomy is the removal of the ovaries, which can both diagnose and treat ovarian cysts by minimally invasive procedure where small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a small camera and surgical instruments to record images that are then displayed on a monitor.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Laparoscopic Myomectomy is the removal of uterine fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. It is the main treatment option for patients who would still like to conceive or prefer not to have a hysterectomy by minimally invasive procedure where small incisions are made in the abdomen over the area where the fibroid is. A camera and surgical instruments are inserted through these incisions to visualize the uterus and act.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids vary depending on their type, size, and position in the uterus. They are most commonly found in women between the ages of 30 to 50 who are still menstruating. Women who begin menstruation before the age of 12 are more likely to develop uterine fibroids. No connection has been found between birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy prescribed for menopause and uterine fibroids. Certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, may increase the risk of uterine fibroids by 24% when compared with women who have normal blood pressure.
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Operative hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat uterine disorders without open surgery. Using a hysteroscope, the uterus can be accessed through the vagina and cervix without any incisions through the abdominal wall.
